MyISAM与InnoDB引擎
首先,Mysql的引擎除了InnoDB和MyISAM还有很多,这两个相对比较出名,5.5以前默认是MyISAM,而5.5以后默认是InnoDB,除了这两个引擎,还有Memory、CSV、Archive、Blackhole等等,具体可以参考官网Alternative Storage Engines。
概述
直接引用官网上的概述:
-
InnoDB: The default storage engine in MySQL 5.7. InnoDB is a transaction-safe (ACID compliant) storage engine for MySQL that has commit, rollback, and crash-recovery capabilities to protect user data. InnoDB row-level locking (without escalation to coarser granularity locks) and Oracle-style consistent nonlocking reads increase multi-user concurrency and performance. InnoDB stores user data in clustered indexes to reduce I/O for common queries based on primary keys. To maintain data integrity, InnoDB also supports FOREIGN KEY referential-integrity constraints.
-
MyISAM: These tables have a small footprint. Table-level locking limits the performance in read/write workloads, so it is often used in read-only or read-mostly workloads in Web and data warehousing configurations.
对于MyISAM的场景说的很明确,“used in read-only or read-mostly workloads in Web and data warehousing configurations.”也就是说在只读的场景中比较合适。而Innodb更适合一般的场景,事务特性,多用户并发等。
比较
MyISAM与InnoDB对两者的比较,参考wikiComparison of MySQL database engines:
- InnoDB recovers from a crash or other unexpected shutdown by replaying its logs. MyISAM must fully scan and repair or rebuild any indexes or possibly tables which had been updated but not fully flushed to disk. Since the InnoDB approach is approximately fixed time while the MyISAM time grows with the size of the data files, InnoDB offers greater availability as database sizes grow.
crash后恢复性能InnoDB较好。
- InnoDB, with innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit set to 1, flushes the transaction log after each transaction, greatly improving reliability.[1] MyISAM has to be run on top of a fully journaled filesystem, such as ext4 mounted with data=journal, to provide the same resilience against data file corruption. (The journal can be put on an SSD device for improved MyISAM performance, similarly, the InnoDB log can be placed on a non-journaled filesystem such as ext2 running on an SSD for a similar performance boost. Reliability is not sacrificed in either case.)
InnoDB在每次事务处理后刷新事务日志,而MISAM需要依赖文件系统才能获得可靠性。
- InnoDB can be run in a mode where it has lower reliability but in some cases higher performance. Setting innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit to 0 switches to a mode where transactions are not committed to disk before control is returned to the caller. Instead, disk flushes happen on a timer.[1]
在批量插入的时候,此配置有用,可以在批量插入结束后关闭此配置。类似的,很多系统都有用可靠性换取速度的配置,如ceph的replica设置,kafka、Hbase返回时最小写入副本数目的设置。
- InnoDB automatically groups together multiple concurrent inserts and flushes them to disk at the same time.[2] MyISAM relies on the filesystem block cache for caching reads to the data rows and indexes, while InnoDB does this within the engine itself, combining the row caches with the index caches.[3]
InnoDB对并行插入有批量flush的操作,类似于Kafka。而MyISAM此操作依赖文件系统。
- InnoDB will store rows in primary key order if present, else first unique key order. This can be significantly faster if the key is chosen to be good for common operations.[citation needed] If there is no primary key or unique key InnoDB will use an internally generated unique integer key and will physically store records in roughly insert order, as MyISAM does. Alternatively, an autoincrementing primary key field can be used to achieve the same effect.
很关键的一点,如果主键是连续的,那么InnoDB在磁盘上插入也是会连续的,这对于插入比较多的场景,主键选取上最好要是单调的,写入速度会有很大提升。
- InnoDB provides updatable LZW compressed page storage for both data and indexes. MyISAM compressed tables can’t be updated.[4]
压缩上,InnoDB的是可更新的。
- When operating in fully ACID-compliant modes, InnoDB must do a flush to disk at least once per transaction, though it will combine flushes for inserts from multiple connections. For typical hard drives or arrays, this will impose a limit of about 200 update transactions per second. For applications which require higher transaction rates, disk controllers with write caching and battery backup will be required in order to maintain transactional integrity. - - InnoDB also offers several modes which reduce this effect, naturally leading to a loss of transactional integrity guarantees, though still retaining greater reliability than MyISAM. MyISAM has none of this overhead, but only because it does not support transactions.
一个关键的数据,对于一般的磁盘设备,1s也就是200多个update事务,因为受到了磁盘IO的限制。
- MyISAM uses table-level locking on updates and deletes to any existing row, with an option to append new rows instead of taking a lock and inserting them into free space. InnoDB uses row-level locking. For large database applications where many rows are often updated, row-level locking is crucial because a single table-level lock significantly reduces concurrency in the database. Both InnoDB and MyISAM support full-text search, with InnoDB gaining full-text index support in MySQL 5.6.4,[5] but the results can be notably different[6]
MyISAM在updates和deletes行的时候,是对表加的锁,而InnoDB是用的行锁,锁的粒度小,并发当然好点。
数据结构比较
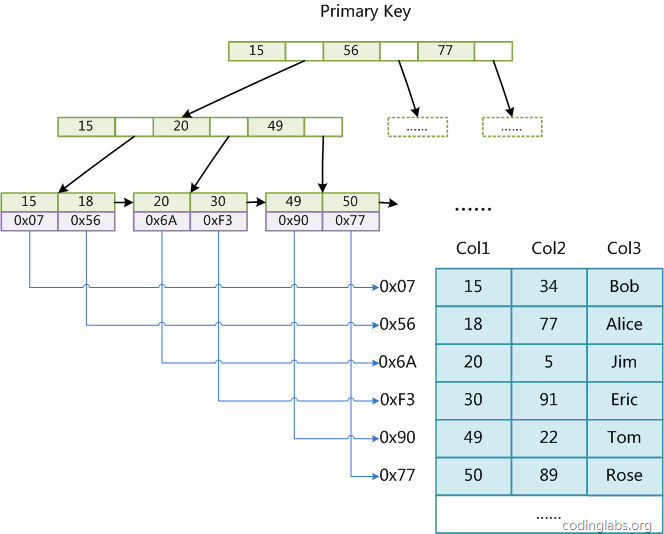
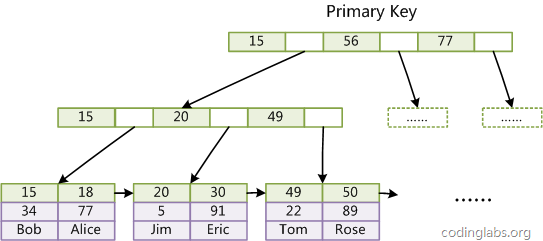
这篇文章MySQL索引背后的数据结构及算法原理对两个引擎数据结构有比较详细的分析,两者都使用了流弊的B+树(Hbase也用B+树),不同点是,MyISAM叶子节点存储的是数据指针,而InnoDB叶子节点直接存储了数据。使用B+树原因是因为要照顾磁盘缓慢的IO速度,而且利用了磁盘预读相对快(顺序读取快)的机制,所以B+树与数据库比较搭配。
MyISAM索引结构:
InnoDB结构:
参考
MyISAM Storage Engine
Introduction to InnoDB
Introduction to InnoDB
MySQL和Lucene索引对比分析