Zuul
what is zuul?
Zuul is an L7 application gateway that provides capabilities for dynamic routing, monitoring, resiliency, security, and more.
就是个L7的网关,nginx也是个L7的网关,其实很多功能与nginx相同。
why build zull?
- Authentication and Security - identifying authentication requirements for each resource and rejecting requests that do not satisfy them.
统一认证和授权,与一般的在api服务中进行认证授权比,这种方式一是能够把认证授权的过程独立在网关中,减少重复工作,微服务对外暴露的服务可能有多个,而多个中可能都有账号的认证授权。而且,有些敏感信息有时候并不期望给后端服务,比如token信息,可以在网关处统一解析token在传递给后端。
第二,在安全性上,能够统一管理对外暴露接口,不是api的所有接口都要对外暴露,典型的就是spring cloude中的acturtor和swagger接口,不期望对外暴露,如果没有这网关,可能就直接暴露给外部访问了。
- Insights and Monitoring - tracking meaningful data and statistics at the edge in order to give us an accurate view of production.
重要是能够很好集成已有的组件,如ribbon和hystrix,利用这些方便、统一监控。
- Dynamic Routing - dynamically routing requests to different backend clusters as needed.
这功能nginx也有,但zuul的功能更灵活,能够通过code的方式配置路由,如通过读取zk上配置的白名单来决定这些请求发送到哪里,这功能也能做一个类似的预览环境,把一些特定的请求,路由到一些特定的服务上。还能够对这些特殊的请求进行debug,把特殊的请求路由到一些debug环境上。
而且能够dynamic routing,通过一个配置中心,线上改变路由参数。
还能做类似的服务分级,如header中增加服务的level,直接路由到对应的level的服务。
- Stress Testing - gradually increasing the traffic to a cluster in order to gauge performance.
压测。通过动态的文件配置,动态增加流量到一个特定小的压测集群,通过收集数据来达到压测的目的。
- Load Shedding - allocating capacity for each type of request and dropping requests that go over the limit.
利用hystrix。
- Static Response handling - building some responses directly at the edge instead of forwarding them to an internal cluster
直接在网关处就处理一些请求,并且response。
- Multiregion Resiliency - routing requests across AWS regions in order to diversify our ELB usage and move our edge closer to our members
多地区的容灾。能通过动态修改配置方式,设置hystrix的fallback方式达到这效果。
基本使用
- 在匹配路径的时候是可以使用?、*、三种方式,?代表一个字符,*代表多个字符一个路径,而代表多级路径。
- zuul默认能够通过server-id的方式进行路径匹配,但是这样会把内部的微服务的信息暴露给外部,如果是对外的api服务,可以禁用ignored-services
- 对于敏感信息,zuul是默认过滤的,sensitive-headers: 如果这样什么也不配置,那么意思就是没有任何的敏感信息头,所有的header都会传递给后端,如果配置了userId,那么会过滤调这个header头。
zuul
Zuul 1.x components:
zuul-core - library which contains the core functionality of compiling and executing Filters
zuul-simple-webapp - webapp which shows a simple example of how to build an application with zuul-core
zuul-netflix - library which adds other NetflixOSS components to Zuul - using Ribbon for routing requests, for example.
zuul-netflix-webapp - webapp which packages zuul-core and zuul-netflix together into an easy to use package
最重要的就是个zuul-core和zuul-netflix,这core里面就是zuul的框架最核心的部分,没有其他的不相干的组件,但是距离应用还缺少些支持。而zuul-netflix把一些必要组件如ribbon和hystrix、服务注册发现、日志等加入,就能集成应用了。
zuul的源码相对简单很多,zuul-core中源码文件也就三四十个,而且都不长,最核心的类,ZuulServlet,本质上看zuul就是个servlet,重写了其中的service方法,代码如下:
@Override
public void service(javax.servlet.ServletRequest servletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
init((HttpServletRequest) servletRequest, (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse);
// Marks this request as having passed through the "Zuul engine", as opposed to servlets
// explicitly bound in web.xml, for which requests will not have the same data attached
RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
context.setZuulEngineRan();
try {
preRoute();
} catch (ZuulException e) {
error(e);
postRoute();
return;
}
try {
route();
} catch (ZuulException e) {
error(e);
postRoute();
return;
}
try {
postRoute();
} catch (ZuulException e) {
error(e);
return;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
error(new ZuulException(e, 500, "UNHANDLED_EXCEPTION_" + e.getClass().getName()));
} finally {
RequestContext.getCurrentContext().unset();
}
}
上面的代码展示了zuul的核心流程,preRoute、route、postRoute,还有个RequestContext,这个RequestContext继承自ConcurrentHashMap,并且每次都是通过getCurrentContext获取一个threadLocal的内部的context,在简单不过了,所有的上下文信息都放在context中,路有前、路由、路由后通过这个context来进行操作。
zuul与zuul2
Zuul 1 was built on the Servlet framework. Such systems are blocking and multithreaded, which means they process requests by using one thread per connection. I/O operations are done by choosing a worker thread from a thread pool to execute the I/O, and the request thread is blocked until the worker thread completes.
zuul通过上面的分析是直接使用的servlet这框架,重写service方法,因为servlet只是个标准,其实底层也通过jetty、或tomcat的nio方式来支持,但这也只能在http的io处理的层次上,而zuul最大的问题是在处理过程中,把request路由到后端服务并等待response的过程是个阻塞的处理的,一个请求需要处理完成才会释放调占用的线程.如下图:
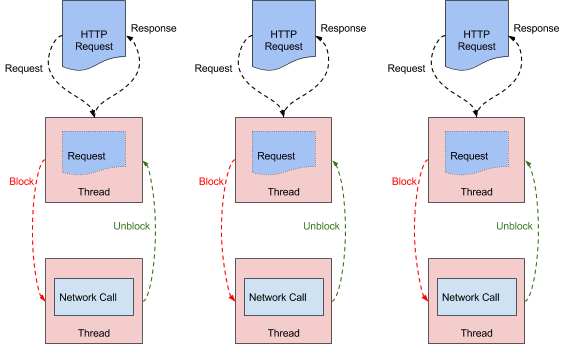
没有看zuul2的源码,但是首先作为一个L7的网关,还是需要解析完http协议的,否则就是个L4的负载均衡,怎么搞肯定不如nginx了,也没啥功能上的优势。异步,是在接收完成http后,发送http的request到后端服务,等待response的过程的,这过程其中最耗时的过程还是局域网IO的过程,然后就是线程上下文切换的过程,也就是对于IO越多,由于IO导致的线上问切换越多那么zuul2带来的性能提升越多。但如果本身网关就要进行很多的计算、加密、解密、压缩等过程,网关本身更多的是CPU密集型的,限制本来就是CPU而不是IO,这个时候zuul2带来的效率就提升不明显了。
After running Zuul 2 in production for the last several months, our evaluation is that the more CPU-bound a system is, the less of an efficiency gain we see.
We have several different Zuul clusters that front origin services like API, playback, website, and logging. Each origin service demands that different operations be handled by the corresponding Zuul cluster. The Zuul cluster that fronts our API service, for example, does the most on-box work of all our clusters, including metrics calculations, logging, and decrypting incoming payloads and compressing responses. We see no efficiency gain by swapping an async Zuul 2 for a blocking one for this cluster. From a capacity and CPU point of view they are essentially equivalent, which makes sense given how CPU-intensive the Zuul service fronting API is.
对于api service,zuul2可能并不能带来性能的提升。
参考
zuul wiki
Announcing Zuul: Edge Service in the Cloud
Zuul 2 : The Netflix Journey to Asynchronous, Non-Blocking Systems