理解token
为什么会有token?
wiki上的定义:
In computer systems, an access token contains the security credentials for a login session and identifies the user, the user’s groups, the user’s privileges, and, in some cases, a particular application.
按照定义,token是个credentials,证书,一个凭证,这东西首先有“书”的特性,记录了一些信息,并不是简单的一个密码,而且不是和session id一样。也可以理解,就是一种信息的格式的约定。
有个Oauth的协议,是需要使用token的也就是说,至少在第三方鉴权的上,这个token是有作用的,能够不把用户密码信息发送给第三方的应用从而安全的简单的进行授权。
另外在app中和web中,现在有了restful,目前应用非常广泛。
JWT是个token的实现的标准,官网的说明:
JSON Web Tokens are an open, industry standard RFC 7519 method for representing claims securely between two parties.
另外在官网上https://jwt.io/也有生成的工具,具体的格式也不复杂,header、payload、verify signature,注意,前两个是Base64编码的并没有加密,第三个verify signature,作用只是验证是不是自己发布的,token有没有被其他人修改过。
为什么header和payload是Base64编码的?
就要求token里面不能存放敏感信息。为什么要Base64?个人感觉还是为了简单,关键token的左右只是个证书,而不是密码的超级加密变种。
而且token有个过期时间,很多时候就是服务端生成个token,然后有效期10分钟,这样的话,如果token被抓到了,岂不是能够模仿用户的行为?是的,token并不能解决这个问题。
token泄漏后还安全么?
不安全。怎么办?推荐使用https,能够保证链路层的的安全,至于客户端包括app和web的token泄露,基本无力解决。
参考OAuth 2.0 Threat Model and Security Considerations
4.1.3. Threat: Obtaining Access Tokens
Depending on the client type, there are different ways that access tokens may be revealed to an attacker. Access tokens could be stolen from the device if the application stores them in a storage device that is accessible to other applications.
Impact: Where the token is a bearer token and no additional mechanism is used to identify the client, the attacker can access all resources associated with the token and its scope.
Countermeasures:
o Keep access tokens in transient memory and limit grants (Section 5.1.6).
o Limit token scope (Section 5.1.5.1).
o Keep access tokens in private memory or apply same protection means as for refresh tokens (Section 5.2.2).
o Keep access token lifetime short (Section 5.1.5.3).
4.4.2.1. Threat: Access Token Leak in Transport/Endpoints
This token might be eavesdropped by an attacker. The token is sent from the server to the client via a URI fragment of the redirect URI. If the communication is not secured or the endpoint is not secured, the token could be leaked by parsing the returned URI.
Impact: The attacker would be able to assume the same rights granted by the token.
Countermeasures:
o The authorization server should ensure confidentiality (e.g., using TLS) of the response from the authorization server to the client (see Section 5.1.1). 4.4.2.2. Threat: Access Token Leak in Browser History
An attacker could obtain the token from the browser’s history. Note that this means the attacker needs access to the particular device.
Countermeasures:
o Use short expiry time for tokens (see Section 5.1.5.3). Reduced scope of the token may reduce the impact of that attack (see Section 5.1.5.1).
o Make responses non-cacheable.
以上,手段只是预防的,如使用https、把token的生命周期搞短、尽量限制token的权限范围、设置浏览器缓存的过期时间。
cookie与token的常用场景
An HTTP cookie (also called web cookie, Internet cookie, browser cookie, or simply cookie) is a small piece of data sent from a website and stored on the user’s computer by the user’s web browser while the user is browsing. Cookies were designed to be a reliable mechanism for websites to remember stateful information (such as items added in the shopping cart in an online store) or to record the user’s browsing activity (including clicking particular buttons, logging in, or recording which pages were visited in the past). They can also be used to remember arbitrary pieces of information that the user previously entered into form fields such as names, addresses, passwords, and credit card numbers.
cookie是浏览器自带的一种文本(通俗),每次发送一个请求浏览器都会自动的在httpheader加入cookie。
cookie的诞生确实是为了解决无状态的问题,但是现在基本不用这个功能了,最重要的就是有大小的限制4k,使用cookie来维持登录态,在实现过程中实际上是在cookie中添加一个token来维持一个登录态。或者cookie中存放个session id。
token,就像开头说的,是个证书,只是代表了一类资源的权限,最典型的的场景就是作为验证后的凭证,免除在一定时间内的重复验证。token的存储和参数传递都需要开发者来处理。
另外一般用token,也可以在后台有对应的用户的session,存储一些回话的状态,但是在大多数情况下,restful的场景,是无状态的,也就是token与状态甚至都没啥关系。
Cookie vs. Token Authentication
主要参考:https://dzone.com/articles/cookies-vs-tokens-the-definitive-guide
首先,这里说的是使用cookie和token使用Authentication的异同,也是cookie和token的常见使用场景,但是并不是表示这两个东西只能这样用,只是一个典型的场景。
一般的交互图:
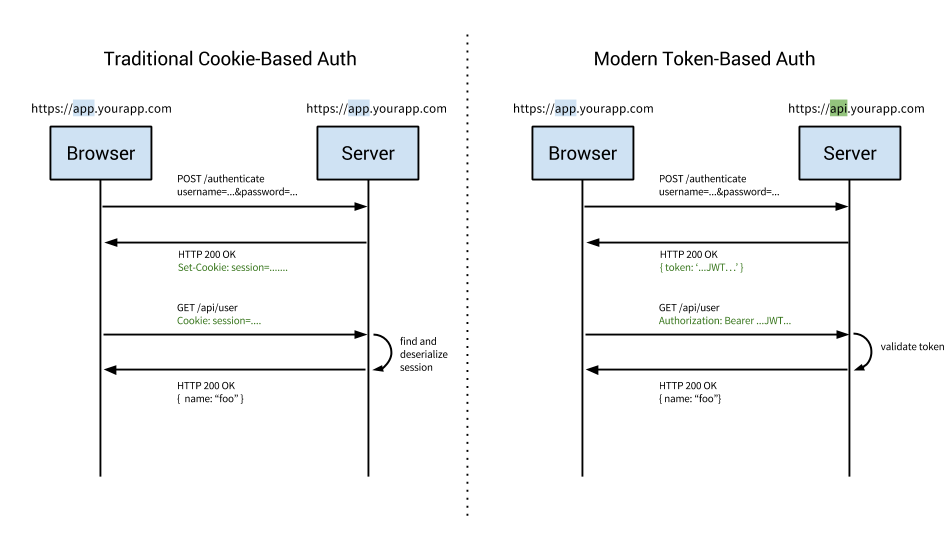
Cookie-based authentication is stateful. This means that an authentication record or session must be kept both server and client-side. The server needs to keep track of active sessions in a database, while on the front-end a cookie is created that holds a session identifier, thus the name cookie based authentication. Let’s look at the flow of traditional cookie-based authentication:
- User enters their login credentials.
- Server verifies the credentials are correct and creates a session which is then stored in a database.
- A cookie with the session ID is placed in the users browser.
- On subsequent requests, the session ID is verified against the database and if valid the request processed.
- Once a user logs out of the app, the session is destroyed both client-side and server-side.
Token-based authentication is stateless. The server does not keep a record of which users are logged in or which JWTs have been issued. Instead, every request to the server is accompanied by a token which the server uses to verify the authenticity of the request. The token is generally sent as an addition Authorization header in the form of Bearer {JWT}, but can additionally be sent in the body of a POST request or even as a query parameter. Let’s see how this flow works:
- User enters their login credentials.
- Server verifies the credentials are correct and returns a signed token.
- This token is stored client-side, most commonly in local storage - but can be stored in session storage or a cookie as well.
- Subsequent requests to the server include this token as an additional Authorization header or through one of the other methods mentioned above.
- The server decodes the JWT and if the token is valid processes the request. Once a user logs out, the token is destroyed client-side, no interaction with the server is necessary.
与传统的cookie认证方式比,使用token的方式有主要两个不同:
- 使用token服务端不需要保存任何的session的信息
- 在logout的时候,只需要在客户端把token给destroy,不需要与服务端进行交互
Advantages of Token-Based Authentication
Stateless, Scalable, and Decoupled
Perhaps the biggest advantage to using tokens over cookies is the fact that token authentication is stateless. The back-end does not need to keep a record of tokens. Each token is self-contained, containing all the data required to check it’s validity as well as convey user information through claims. The server’s only job, then, becomes to sign tokens on a successful login request and verify that incoming tokens are valid. In fact, the server does not even need to sign tokens. Third party services such as Auth0 can handle the issuing of tokens and then the server only needs to verify the validity of the token.
最核心的优点就是,stateless,后端服务不用保存token,而且理想情况下是self-contained,“containing all the data required to check it’s validity as well as convey user information through claims”。自己理解,这self-contained包括两层意思,一是能够包含信息能够验证这个token是有效的,而是包含关键的信息,如用户名、甚至是该用户的的权限信息如能够方位的url信息。与使用cookie的传统的方式比,cookie中里面有session信息,然后需要服务端存储session,然后在找到session对应的用户名,而token里面直接包括了用户名信息,无需服务端保存,也就是服务端的无状态。
Store Data in the JWT
With a cookie based approach, you simply store the session id in a cookie. JWT’s, on the other hand, allow you to store any type of metadata, as long as it’s valid JSON. The JWT spec specifies different types of claims that can be included such as reserved, public and private. You can learn more about the specifics and the differences between the types of claims on the jwt.io website.
In practice, what this means is that a JWT can contain any type of data. Depending on your use case you may choose to make the minimal amount of claims such as the user id and expiration of the token, or you may decide to include additional claims such as the user’s email address, who issued the token, scopes or permissions for the user, and more.
token能够存储各种type的数据。
Performance
When using the cookie-based authentication, the back-end has to do a lookup, whether that be a traditional SQL database or a NoSQL alternative, and the round trip is likely to take longer compared to decoding a token. Additionally, since you can store additional data inside the JWT, such as the user’s permission level, you can save yourself additional lookup calls to get and process the requested data.
For example, say you had an API resource /api/orders that retrieves the latest orders placed via your app, but only users with the role of admin have access to view this data. In a cookie based approach, once the request is made, you’d have one call to the database to verify that the session is valid, another to get the user data and verify that the user has the role of admin, and finally a third call to get the data. On the other hand, with a JWT approach, you can store the user role in the JWT, so once the request is made and the JWT verified, you can make a single call to the database to retrieve the orders.
主要是实现方式上能够提高效率,上面举得例子能够很好的说明,在访问一个页面的时候,甚至可以把次用的角色放在token中,避免了通过数据库查询,判断的过程。
Mobile Ready
Modern APIs do not only interact with the browser. Written properly a single API can serve both the browser and native mobile platforms like iOS and Android. Native mobile platforms and cookies do not mix well. While possible, there are many limitations and considerations to using cookies with mobile platforms.
Common Questions and Concerns
JWT Size
You can store the token in a cookie instead, but the max size of a cookie is only 4kb so that may be problematic if you have many claims attached to the token. Additionally, you can store the token in session storage which is similar to local storage but is cleared as soon as the user closes the browser.
并没有强制JWT的大小最大是多少,但是一定不要太大,因为几乎每次发送的请求都会带这个token。
XSS and XSRF Protection
能够很好的防止XSRF攻击。
Tokens Are Signed, Not Encrypted
token只是一种签名,一般是非对称加密的方式,服务器加密给客户端,然后服务器来验证是否是自己发布出去的。如果要再token中放置敏感信息(一般没有必要)需要通过其他手段。
参考
Oauth的access token 安全么?
app开发token、cookie的区别,账号密码加密又是如何保证安全?
理解OAuth 2.0
Oauth协议rfc
会话是否真的违反RESTfulness?
What is a cookie?
聊一聊 cookie
Cookies vs. Tokens: The Definitive Guide