Hystrix
What is Hystrix?
In a distributed environment, inevitably some of the many service dependencies will fail. Hystrix is a library that helps you control the interactions between these distributed services by adding latency tolerance and fault tolerance logic. Hystrix does this by isolating points of access between the services, stopping cascading failures across them, and providing fallback options, all of which improve your system’s overall resiliency.
git上的参考,Hystrix只是一个library(与vue和react一样),主要解决调用服务时时延、错误问题,防止级联故障,提高系统的overall resiliency。
What Is Hystrix For?
Hystrix is designed to do the following:
- Give protection from and control over latency and failure from dependencies accessed (typically over the network) via third-party client libraries.
- Stop cascading failures in a complex distributed system.
- Fail fast and rapidly recover.
- Fallback and gracefully degrade when possible.
- Enable near real-time monitoring, alerting, and operational control.
最重要的就是Stop cascading failures 这个特性。辅助监控还有告警、在线配置修改等。
以上是Hystrix提供的功能,如果没有Hystrix,那么作为一个service提供给三方用的client,优先级从高到低需要哪些功能?
- 超时,这个是必不不可少的。给调用方用的client需要有的最最基本的功能,没有超时非常容易系统级联故障。
- 控制并发数。,如果没有此功能,超时配置不当,会造成占用大量调用方的资源,一个业务接口耗尽整个容器的用户线程。当然达到预设的并发需要通过异常方式通知调用方。
- 监控,包括调用的时延、P99、P99.9等,还有成功的次数、失败的次数等。
- fallback,在超时失败时候提供的兜底策略的扩展。
- 熔断机制
- 熔断后自动恢复机制
What Design Principles Underlie Hystrix?
- Preventing any single dependency from using up all container (such as Tomcat) user threads.
- Shedding load and failing fast instead of queueing.
- Providing fallbacks wherever feasible to protect users from failure.
- Using isolation techniques (such as bulkhead, swimlane, and circuit breaker patterns) to limit the impact of any one dependency.
- Optimizing for time-to-discovery through near real-time metrics, monitoring, and alerting
- Optimizing for time-to-recovery by means of low latency propagation of configuration changes and support for dynamic property changes in most aspects of Hystrix, which allows you to make real-time operational modifications with low latency feedback loops.
- Protecting against failures in the entire dependency client execution, not just in the network traffic.
设计原则,可以分为两大类,总体原则,和问题监控、问题发生处理、问题恢复这个逻辑每个步骤的处理原则。
- 问题监控:通过进实时的监控、告警发现问题。
- 问题发生处理,主要三点:通过减少负载、failing fast而不是入队方式保护系统;尽可能使用fallback 处理用户请求失败;通过隔离技术来减少问题点对系统的影响。
- 问题恢复:主要是低延迟的在线配置。其实从断路器的状态变化,也是问题恢复重要方式。
- 总体原则,主要两点:防止单个依赖耗尽用户线程;处理的是调用的整个声明周期的错误,而不只是网络,包括其他任何原因导致的接口耗时过长、失败等。
How Does Hystrix Accomplish Its Goals?
Wrapping all calls to external systems (or “dependencies”) in a HystrixCommand or HystrixObservableCommand object which typically executes within a separate thread (this is an example of the command pattern).
“typically executes within a separate thread”,官方都这么说,看来使用信号量控制的方式确实是非主流。
Timing-out calls that take longer than thresholds you define. There is a default, but for most dependencies you custom-set these timeouts by means of “properties” so that they are slightly higher than the measured 99.5th percentile performance for each dependency.
这里设置的虽然建议是99.5的时间,但意思并不是超过99.5后就触发熔断,这里99.5是超时后通过fallback给用户通过服务。
Maintaining a small thread-pool (or semaphore) for each dependency; if it becomes full, requests destined for that dependency will be immediately rejected instead of queued up.
“each dependency”这里理解可能是一个服务,但也可以理解为一个服务的一个接口。在一个服务内,如果服务有很多接口,其中一个接口调用量非常大,可以单独搞出一个“ a small thread-pool (or semaphore)”。
Measuring successes, failures (exceptions thrown by client), timeouts, and thread rejections.
统计的不仅仅是成功、失败、超时,还有rejections,在断路器状态转化会使用此参数。
Tripping a circuit-breaker to stop all requests to a particular service for a period of time, either manually or automatically if the error percentage for the service passes a threshold.
Tripping意思是跳闸,就是家里的空开跳闸,正常情况下是close的。
Performing fallback logic when a request fails, is rejected, times-out, or short-circuits.
fallback的时机,与断路器的状态并无绝对的关系,在断路器open、half-open、close下都会有fallback,在close状态下,请求的超时、错误,或者半开下的rejected,或者short-ciruits(open)都会有fallback。
Monitoring metrics and configuration changes in near real-time.
监控、配置都是近实时的。
PS: 真的断路器,参考wiki是没有什么half-open状态的。而且一般不会自动恢复,都是手动恢复的。
Hystrix流程图
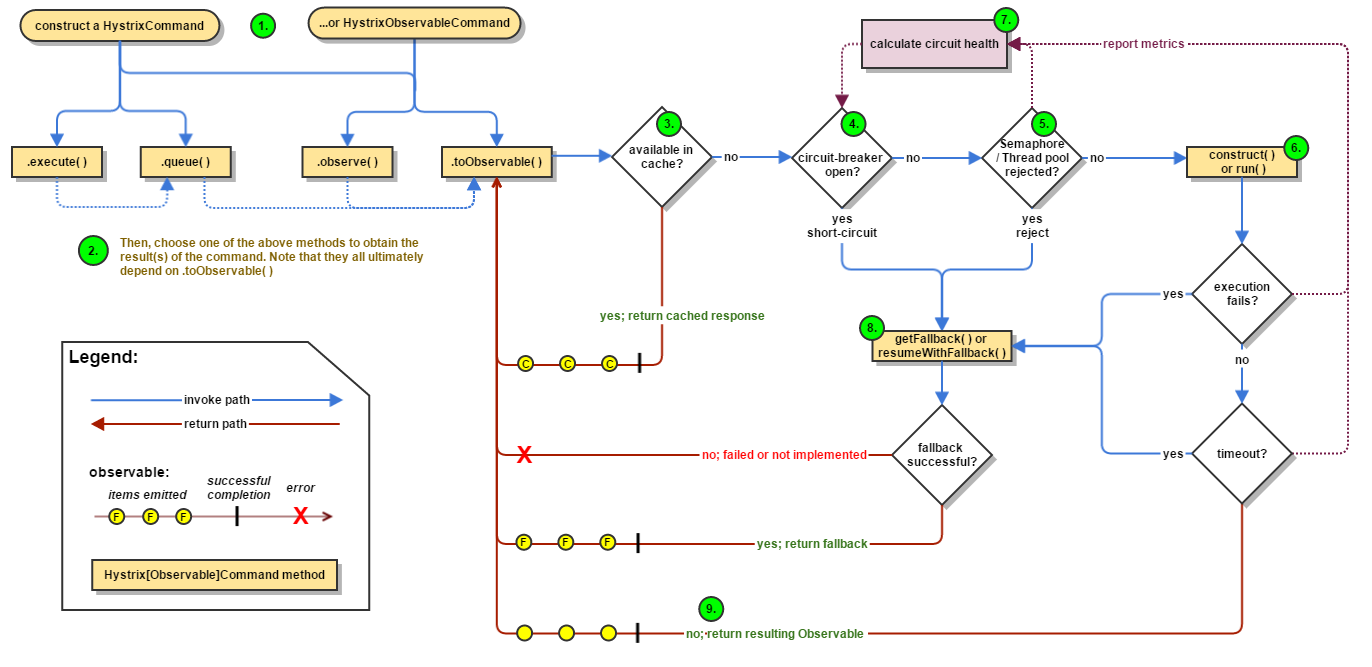
具体步骤Flow Chart
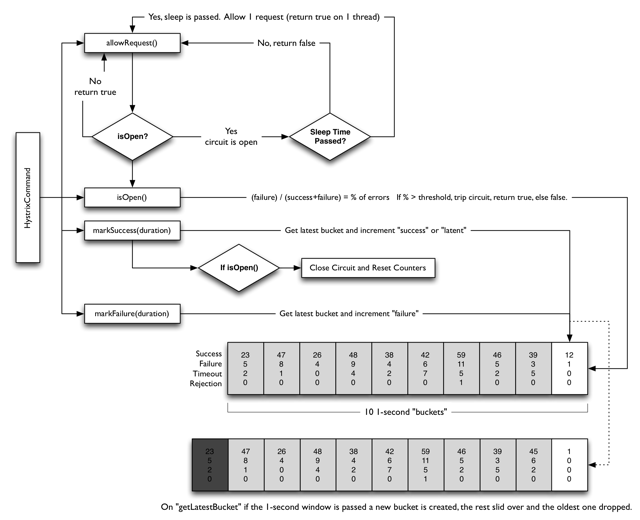
断路器工作流程图
核心指标
- 快照时间窗
- 请求总数阈值
- 错误百分比
快照时间窗
快照时间窗,Hystrix的监控类似滑动窗口,但是又不相同,窗口是由多个buckets组成的,每个buckets是一个小的时间段,里面记录了这段时间内请求Success、Failure、Timeout、Rejection的个数,这样维护一个小的buckets,然后根据先进先出的原则进行淘汰,把buckets维护在一个固定的总数,这样把一个时间连续的数据,变成一个个离散的个数有限的buckets,与模拟信号数字化的过程很像,每个buckets相当于一个采样点。
这样做最主要就是进行动态的统计,能复用以前的统计结果,比如10秒内,每一秒一个bucket,那么第11秒的时候,第1秒的buckets就丢弃掉,但是第2到第10秒的统计的bucket还能复用,与第11秒的bucket结合,就能统计出最近十秒内,总共的请求的个数,和各个请求失败、超时站的百分比了。
请求总数阈值
请求总数阈值,能防止在系统刚启动时候的不稳定,比如20秒有40个请求才会进行判断,防止比如第一次请求就失败,那错误概率就是100%,这样会立刻熔断启动就启动不起来了。从统计学上看,如果统计的个数太少,那么统计不具有典型的意义,需要统计样本到达一定的数量,才能反应一般的问题。
错误百分比
主要通过异常来统计。
半开启状态
后端服务在出现问题的时候,也会恢复,这个时候熔断器也需要相应的机制去恢复到闭合,默认情况下,熔断器在开启5秒后进入半开启状态。在半开状态,会放行一次请求到后端,如果成功,那么熔断器就close,如果失败就继续熔断open。
线程池 or 信号量?
Hystrix支持两种隔离方式,线程池方式和信号量方式。线程池优点:支持超时、支持异步(walk away),信号量优点:新能好,无线程池开销。
虽然线程池方式支持异步,但是很多情况下不会使用此特性,除非对性能要求较高的场景。但是,只区区这一点:支持超时,已经足够。接口超时是调用过程中非常常见的情况,而且不考虑此情况,可能对系统影响极大。如有有人刻意构造出的慢请求,如果没有超时处理,那么很快,会达到隔离并发的上限,导致依赖服务不可用。看看官方如何描述的吧:
You can use semaphores (or counters) to limit the number of concurrent calls to any given dependency, instead of using thread pool/queue sizes. This allows Hystrix to shed load without using thread pools but it does not allow for timing out and walking away. If you trust the client and you only want load shedding, you could use this approach.
比如一个服务只是对Redis的访问,提供一个client,可以通过信号量的方式。
线程池参数
线程池默认的线程数目为10,coreSize与maximum都为10,线程keep alive为1分钟,,在以下类中
public abstract class HystrixThreadPoolProperties {
/* defaults */
static int default_coreSize = 10; // core size of thread pool
static int default_maximumSize = 10; // maximum size of thread pool
static int default_keepAliveTimeMinutes = 1; // minutes to keep a thread alive
static int default_maxQueueSize = -1; // size of queue (this can't be dynamically changed so we use 'queueSizeRejectionThreshold' to artificially limit and reject)
// -1 turns it off and makes us use SynchronousQueue
static boolean default_allow_maximum_size_to_diverge_from_core_size = false; //should the maximumSize config value get read and used in configuring the threadPool
//turning this on should be a conscious decision by the user, so we default it to false
static int default_queueSizeRejectionThreshold = 5; // number of items in queue
static int default_threadPoolRollingNumberStatisticalWindow = 10000; // milliseconds for rolling number
static int default_threadPoolRollingNumberStatisticalWindowBuckets = 10; // number of buckets in rolling number (10 1-second buckets)
...
}
其中
static int default_maxQueueSize = -1; // size of queue (this can’t be dynamically changed so we use ‘queueSizeRejectionThreshold’ to artificially limit and reject) // -1 turns it off and makes us use SynchronousQueue
如上所说,主要原因是阻塞队列的maxQueue不能“can’t be dynamically changed so we use ‘queueSizeRejectionThreshold’”,默认情况下使用default_queueSizeRejectionThreshold 来作为队列中的最大数,超过这个数目就会reject。
default_allow_maximum_size_to_diverge_from_core_size这个配置默认为false,如果想修改线程池的maxmumsize,配置参数的时候需要修改这个参数为true。
HystrixRuntimeException类型
public class HystrixRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5219160375476046229L;
private final Class<? extends HystrixInvokable> commandClass;
private final Throwable fallbackException;
private final FailureType failureCause;
public static enum FailureType {
BAD_REQUEST_EXCEPTION, COMMAND_EXCEPTION, TIMEOUT, SHORTCIRCUIT, REJECTED_THREAD_EXECUTION, REJECTED_SEMAPHORE_EXECUTION, REJECTED_SEMAPHORE_FALLBACK
}
...
}
All exceptions thrown from the run() method except for HystrixBadRequestException count as failures and trigger getFallback() and circuit-breaker logic.
如果抛出的为用户异常,会转成这个这个COMMAND_EXCEPTION异常么?
如果结合feigh使用,会如何转换异常?
Command Group And Command Thread-Pool
Hystrix uses the command group key to group together commands such as for reporting, alerting, dashboards, or team/library ownership.
By default Hystrix uses this to define the command thread-pool unless a separate one is defined.
The thread-pool key represents a HystrixThreadPool for monitoring, metrics publishing, caching, and other such uses. A HystrixCommand is associated with a single HystrixThreadPool as retrieved by the HystrixThreadPoolKey injected into it, or it defaults to one created using the HystrixCommandGroupKey it is created with.
并不是一个service一定对应一个Command Group(Command Thread-Pool),一个service中的两个接口,可以有相同的Command Group、不同的Command Thread-Pool,不同的Command Thread-Pool有相同的Command Group是为了统计方便。
The reason why you might use HystrixThreadPoolKey instead of just a different HystrixCommandGroupKey is that multiple commands may belong to the same “group” of ownership or logical functionality, but certain commands may need to be isolated from each other.
这可以看出,“HystrixCommandGroupKey”更多偏向组织结构层,那个组维护的服务,而即使是一个组提供的服务,不同的接口之间也可能需要隔离。
 参考:
参考: